- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
How Are ESD Tweezers Important in Precision Work?
2025-09-23
In the world of precision work—whether in electronics, laboratory testing, or watchmaking—small details make the biggest difference. One such detail is the choice of tools, and among them, the ESD tweezer has become indispensable.
ESD tweezers, or Electrostatic Discharge tweezers, are precision tools specifically designed to handle sensitive electronic components without the risk of electrostatic damage. Electrostatic discharge can be invisible to the human eye yet powerful enough to destroy or degrade delicate circuits, microchips, and other sensitive devices. Unlike conventional tweezers made solely for gripping, ESD tweezers are manufactured from materials that either dissipate static charges or prevent them from accumulating altogether.
The core purpose of an ESD tweezer is to ensure safe handling, precision, and protection. From assembly lines of consumer electronics to research labs developing next-generation microprocessors, ESD tweezers play a protective role that keeps costly and fragile parts intact.
Professionals working with microelectronics understand the risk: a static spark as small as 100 volts can damage a semiconductor. Humans can only feel shocks above 3000 volts, which means damage can occur long before we are aware. This is where ESD tweezers make the difference—protecting investments, ensuring accuracy, and maintaining production quality.
To gain a better technical overview, here is a structured look at their parameters:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | ESD Tweezer |
| Material Options | Carbon steel, stainless steel, ceramic tips, conductive plastic |
| Length Range | 110 mm – 140 mm |
| Surface Resistance | 10⁴ – 10⁹ ohms (depending on model type) |
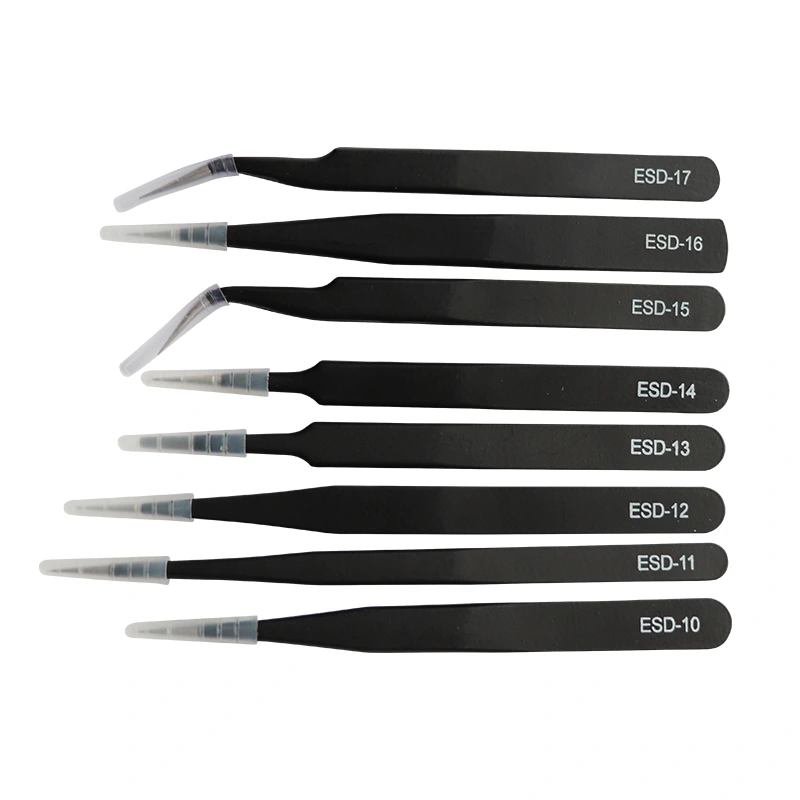
| Tip Variations | Straight, curved, angled, ultra-fine, blunt |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 300 °C (ceramic tips for high-heat environments) |
| Anti-Magnetic Property | Available in selected stainless steel and ceramic models |
| Application Areas | Electronics assembly, PCB handling, laboratory testing, watchmaking, optics |
| Key Function | Safe handling of sensitive components by preventing static discharge |
This combination of parameters shows why ESD tweezers are not just tools—they are part of a broader strategy for safety, precision, and efficiency in demanding industries.
Why Are ESD Tweezers the Preferred Choice for Professionals?
Electronics and micro-assembly industries are built on reliability, and even the smallest compromise can lead to large-scale product failure. So why are ESD tweezers prioritized over traditional tweezers?
1. Protection Against Electrostatic Damage
Every electronic component is vulnerable to static discharge. A single uncontrolled spark can permanently weaken or destroy semiconductors. ESD tweezers eliminate this risk by dissipating static charges safely. This protection is essential not only during manufacturing but also during inspection and repair.
2. Superior Precision for Delicate Components
ESD tweezers come with highly specialized tips, ranging from ultra-fine to wide blunt tips, enabling professionals to handle minute parts such as surface-mount devices (SMDs), watch gears, or micro-optical components. This precision improves assembly quality and reduces error rates.
3. Versatility Across Multiple Industries
Although most associated with electronics, ESD tweezers are valuable across:
-
Medical device manufacturing: handling tiny surgical implants or instruments.
-
Watchmaking and jewelry: ensuring precision without scratches or contamination.
-
Research laboratories: managing fragile samples under controlled conditions.
4. Enhanced Ergonomics and Worker Safety
Modern ESD tweezers are designed with ergonomics in mind, reducing fatigue during long hours of repetitive tasks. This not only improves worker comfort but also enhances accuracy and consistency in production environments.
5. Cost Efficiency and Reliability
By preventing electrostatic damage, companies save significantly on rejected parts, rework, and warranty claims. In high-volume production, the long-term savings from using ESD tweezers are substantial.
In short, the "why" behind ESD tweezers is simple: they protect investments, enhance precision, and secure operational efficiency. Without them, the risks of costly product failure would increase dramatically.
How Are ESD Tweezers Designed and Applied in Real-World Settings?
The “how” of ESD tweezers lies in both their design and their practical usage across industries.
How They Are Designed
ESD tweezers are engineered with specific features to meet industrial needs:
-
Material composition: Conductive or dissipative materials prevent static buildup. Stainless steel and ceramics are commonly used, with ceramic tips offering high-temperature resistance and non-magnetic qualities.
-
Surface coating: Anti-static coatings add extra protection and ensure durability.
-
Tip variety: Curved, angled, or ultra-fine tips are designed for specialized applications, such as soldering, micro-assembly, or delicate repairs.
-
Resistance control: Surface resistance is engineered to fall within safe ranges (10⁴–10⁹ ohms), preventing sudden discharges.
How They Are Applied
Across industries, the application of ESD tweezers includes:
-
Electronics assembly lines: Placing microchips on circuit boards with ultra-fine tweezers.
-
Laboratory research: Handling fragile samples in cleanroom environments.
-
Repair stations: Safely replacing damaged electronic parts without causing further harm.
-
Watchmaking workshops: Securing tiny gears with precision tools that avoid scratches or static shocks.
The application is not just about holding parts—it’s about ensuring quality and safety in every step.
Best Practices for Using ESD Tweezers
-
Always pair tweezers with ESD-safe mats, wrist straps, and grounded workstations.
-
Store tweezers in anti-static cases when not in use.
-
Choose the correct tip shape for the job to avoid slippage or damage.
-
Inspect regularly for wear, as damaged tips can compromise both precision and safety.
When designed and used correctly, ESD tweezers become an extension of the professional’s skill, ensuring that the tiniest details are handled with care.
How Can Businesses Benefit by Choosing the Right ESD Tweezer Partner?
For businesses, selecting the right ESD tweezer is not only a matter of tool choice—it’s a matter of operational reliability, brand reputation, and long-term cost savings.
Business Advantages of ESD Tweezers
-
Reduced Product Failures: Preventing electrostatic damage lowers the number of defective products.
-
Improved Production Quality: Precision tools allow for cleaner, more accurate assembly.
-
Compliance with Standards: Many industries require adherence to ESD safety protocols, which include using approved tools.
-
Scalable Efficiency: In high-volume manufacturing, even small improvements in handling translate into major efficiency gains.
Integrating ESD Tweezers into Workflow
Businesses can enhance productivity by training staff on proper ESD practices, pairing tweezers with other protective equipment, and ensuring tool replacement cycles are managed proactively. A well-structured ESD management program prevents downtime and ensures compliance with international standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between regular tweezers and ESD tweezers?
Regular tweezers are designed for gripping but do not protect against static charges. ESD tweezers are made from dissipative or conductive materials that prevent electrostatic buildup, making them safe for handling sensitive electronics.
Q2: How do I choose the right type of ESD tweezer for my work?
The right tweezer depends on the task: ultra-fine tips are ideal for microchip placement, curved tips work well for angled assembly, ceramic tips are best for high-temperature work, and blunt tips are suitable for general handling. Always consider both material and tip design.
From their ability to prevent electrostatic damage to their unmatched precision in delicate assembly tasks, ESD tweezers are more than just tools—they are vital instruments for professionals across electronics, laboratories, and precision engineering. They safeguard components, streamline operations, and ensure compliance with industry standards, making them an investment every business can rely on.
For companies looking to source high-quality ESD tweezers with proven reliability, Xin Lida stands out as a trusted provider, offering a wide range of solutions designed to meet global demands. To discover how our ESD tweezer solutions can support your business growth and precision requirements, we encourage you to contact us today for more information and tailored support.